
₹7,000.00 Original price was: ₹7,000.00.₹2,999.00Current price is: ₹2,999.00.

When starting a business in India with a partner, one of the most important things you need to do is create a partnership deed. But what exactly is a partnership deed, and why is it so important? Let’s break it down in simple terms. A partnership deed is a legal document that lays out the rules, roles, and responsibilities of each partner in a business. It’s essentially a blueprint for how the business will operate, and it ensures that everyone involved is on the same page. While this might sound serious, think of it as the foundation of a healthy, long-term business relationship.
Partnerships are a popular way to start and grow businesses in India because they allow entrepreneurs to pool their resources, skills, and ideas. However, without a clear framework, misunderstandings and conflicts can arise. This is where a partnership deed comes in. It helps avoid disputes by clearly defining who does what, who gets what, and how decisions are made. Let’s dive into why a partnership deed is so crucial for any business partnership in India and how it can save you from future headaches.
At its core, a partnership deed is a formal agreement between two or more business partners. It is a written document that defines the roles, responsibilities, profit-sharing arrangements, and other key aspects of how the partnership will work. It’s like a roadmap that guides the day-to-day functioning of the business. Without it, you might find yourself navigating tricky situations without a clear direction.
In India, the Indian Partnership Act of 1932 governs the creation and regulation of partnerships. While a partnership can technically be formed without a deed, having one in writing is strongly recommended. A written partnership deed provides clarity, and it can be used as legal evidence in case of any disputes. So, even if things are going smoothly right now, having this document in place can give you peace of mind for the future.
You may be wondering, “Why is a partnership deed so important?” Well, imagine running a business with a partner but never discussing who’s responsible for what or how you’ll share the profits. Sounds like a recipe for disaster, right? A partnership deed helps prevent these kinds of problems by providing structure. It formalizes every partner’s duties, rights, and obligations, making sure that everyone knows exactly what’s expected of them.
Another crucial aspect of a partnership deed is that it lays out how the profits and losses will be shared among the partners. This can save you from a lot of arguments down the road. Whether the partners are contributing equally or one partner is investing more capital or effort, the deed can specify exactly how profits will be divided. This transparency ensures fairness and prevents misunderstandings.
Furthermore, a partnership deed can include provisions for what happens if one partner decides to leave or if a new partner wants to join. It can also address what will happen in case of the unfortunate demise of one of the partners. These scenarios might be difficult to think about now, but addressing them in your partnership deed ensures that your business will continue to run smoothly, no matter what the future holds.
There are three distinct types of partnership deeds:
Each type of partnership agreement serves to establish the framework for the partnership’s operation and the extent of liability borne by the partners, offering flexibility in structuring business relationships.
Creating a partnership deed is like laying the groundwork for a strong business relationship. A well-drafted deed should contain certain key clauses that outline how the partnership will function. These clauses provide clarity and direction, ensuring that everyone involved knows what to expect. While drafting your partnership deed might feel like a tedious task, it’s worth it to make sure everything is crystal clear. Let’s take a look at the key clauses every partnership deed must have, including profit-sharing, partner duties, and the all-important termination clause.
Let’s face it—one of the main reasons we get into business is to make a profit. So, it’s essential that your partnership deed has a clear profit-sharing clause. This clause defines how profits (and losses) will be divided among partners. You might decide to split everything equally, or you may prefer a ratio that reflects each partner’s investment or contribution to the business.
Whatever your arrangement, the profit-sharing clause should be specific to avoid any future misunderstandings. For example, it can state whether profits are divided monthly, quarterly, or annually. If a partner has contributed more capital or takes on more responsibilities, the deed should clearly reflect this by adjusting their share of the profits accordingly. This is where you make sure that everyone feels fairly compensated for their hard work, and no one’s left grumbling at the end of the day.
Running a business is much smoother when everyone knows their role. This is why the duties and responsibilities clause is crucial. Think of it as your business’s job description section, ensuring that each partner understands what they are responsible for.
In this clause, you’ll outline what each partner is expected to do. Are they in charge of daily operations? Or are they more of a silent partner who contributes financially but doesn’t handle the business’s day-to-day activities? This can also include specifics, such as managing the company’s accounts, handling client relationships, or making executive decisions. By detailing each partner’s responsibilities, you’re preventing confusion, finger-pointing, and stress down the road. You’ll thank yourself later for being clear right from the start.
This clause can also help when a partner isn’t pulling their weight. If it’s clear who’s supposed to do what, there’s no argument over who dropped the ball when things go wrong. The partnership deed serves as a reference point to keep everyone accountable.
Ah, decision-making—the heartbeat of any business. In a partnership, how decisions get made is just as important as the decisions themselves. The decision-making clause is where you outline how business choices will be handled. Will all partners have an equal vote on every matter? Or will some partners have more influence than others, depending on their role or financial contribution?
You can also specify what type of decisions need unanimous consent and which can be made by a majority vote. Maybe smaller, day-to-day matters can be handled by the managing partner, while big decisions—like expanding the business—require everyone’s input. The last thing you want is for decision-making to become a tug-of-war. This clause ensures smooth sailing when it comes to steering the ship.
This clause tackles the all-important question: Who’s bringing in the money? The capital contribution clause is where you outline how much each partner is investing in the business, whether it’s cash, assets, or even expertise. This clause helps avoid any confusion down the line about who has put in what and ensures that everything is transparent from the get-go.
By clearly specifying each partner’s contribution, you can link it back to other clauses like profit-sharing and voting rights. If one partner is putting in more capital, they might expect a larger share of the profits or more voting power in decisions. Getting this down on paper will prevent any awkward conversations about money in the future.
No one likes to think about the end when everything’s just getting started, but a solid partnership deed includes a termination clause just in case things don’t go as planned. This clause outlines the process for dissolving the partnership, whether it’s due to a partner leaving, retirement, or even a disagreement.
The termination clause should cover how the partnership’s assets will be divided and how liabilities will be handled. It should also specify what happens if a partner wants to exit the business, as well as the steps required to bring in a new partner. It’s like the emergency escape plan of your business partnership—it’s always good to know it’s there, even if you never need it.
Let’s be honest—disagreements happen, even in the best partnerships. The dispute resolution clause is where you’ll outline how conflicts will be resolved without derailing the entire business. Whether it’s through mediation, arbitration, or simply a majority vote, having a clear process in place can save everyone time, money, and frustration. This clause ensures that, even when disagreements arise, there’s a plan in place to settle things quickly and efficiently.
This doesn’t just keep the peace between partners; it also keeps the business running smoothly. After all, the longer a dispute drags on, the more the business suffers. Having a pre-agreed method for resolving conflicts will help keep emotions in check and allow for more objective decision-making.
Drafting a partnership deed might seem straightforward at first, but many business owners make mistakes that can come back to bite them later. The last thing you want is to find out your agreement has a legal loophole when you’re deep into running your business. But don’t worry—it’s easier than you think to avoid these common pitfalls once you know what to watch out for. Here, we’ll walk you through some of the most common mistakes in drafting deeds and offer tips on how to avoid them, so you can rest easy knowing your agreement is rock solid.
One of the most common mistakes people make when drafting partnership deeds is not being clear about profit-sharing. Imagine going through all the hard work, only to argue over how profits should be split. It sounds stressful, doesn’t it? That’s why it’s crucial to avoid vague profit-sharing clauses that leave room for interpretation.
Don’t just assume that everyone’s going to “figure it out later”—spelling it out from day one is much better. Be specific! Will the profits be split equally, or will it be based on capital contribution or workload? Whatever the decision, make sure it’s clear in the deed. This will prevent any confusion when the time comes to divide up the earnings and keep everyone happy.
Another mistake that can create chaos is failing to clearly define roles and responsibilities in the partnership deed. Without a clear division of duties, you might end up with one partner doing all the work while others slack off. Or, even worse, no one does anything because everyone thinks it’s someone else’s job!
Avoid this by ensuring that each partner’s role is clearly outlined. This includes not only day-to-day tasks but also who’s responsible for key decisions and who handles specific areas of the business. By breaking down responsibilities, you’ll keep everything running smoothly and avoid the dreaded “But I thought you were doing that!” conversation.
No one likes to think about disagreements when they’re just starting a new venture, but ignoring dispute resolution is a big mistake. Conflicts are bound to happen in any business, no matter how strong the relationship between partners. If your partnership deed doesn’t include a dispute resolution clause, you could be setting yourself up for long, drawn-out arguments.
It’s best to have a plan in place for how you’ll handle conflicts from the start. Whether you choose arbitration, mediation, or a voting system, having a clear method for resolving disputes will save you a lot of headaches down the road. By planning for peace, you’re preparing for any bumps that might come along the way.
Here’s a common mistake that many business owners overlook: not having an exit strategy in the partnership deed. What happens if one partner wants to leave the business? Or worse, what if a partner suddenly passes away? These are tough scenarios to think about, but having an exit strategy in place is essential for protecting the business.
Make sure your deed includes provisions for how to handle situations where a partner wants out. Will the remaining partners buy their share? Can they sell it to someone else? What if a new partner wants to join? Covering all these bases ensures that your business will survive, no matter what happens with individual partners.
Life happens, businesses grow, and partnerships evolve, but many people forget to update their partnership deed to reflect these changes. This is one of the most common pitfalls that can lead to legal trouble. An outdated deed might not reflect the current state of the business or the partners’ responsibilities.
To avoid this, make it a habit to review and update your partnership deed periodically. If you’ve added new partners, changed your profit-sharing arrangement, or expanded the business, it’s time to revise the deed. This simple step keeps everything relevant and ensures that your agreement stays watertight as your business evolves.
It’s easy to get caught up in the excitement of starting a business and overlook legal formalities when drafting a partnership deed. But failing to follow the proper legal processes can lead to problems down the line. For instance, not registering the deed, not paying stamp duty, or using vague legal language can create legal loopholes that might be exploited later.
Always ensure that your deed is drafted in compliance with the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, and that you’ve followed the necessary legal steps to make it enforceable. Consulting with a legal expert during the drafting process can help you avoid cutting corners and ensure that the deed holds up in court if needed.
A partnership agreement serves as a safeguard for your interests in case of disputes or confusion regarding various matters within the partnership. Therefore, the Deed should encompass all the legal details related to the firm. Although there isn’t a standardized format for drafting a Partnership Deed, we’ve compiled a list of essential information typically found in a partnership agreement to provide you with an overview:
It is also called a provisions of partnership deed, which are specific clauses that detail the business venture’s rights, responsibilities, profit-sharing, and overall operation. Including these provisions helps ensure a smooth partnership by clearly outlining expectations for each partner.
To register a partnership in India, you’ll need to fill out Form A, which is the official application for partnership registration. You can download this form from your local Registrar of Firms website, or you can pick up a physical copy at the Registrar’s office. Filling out the form is pretty straightforward—it asks for basic details about your partnership, like:
Make sure all the details match what’s written in your partnership deed to avoid any issues during registration.
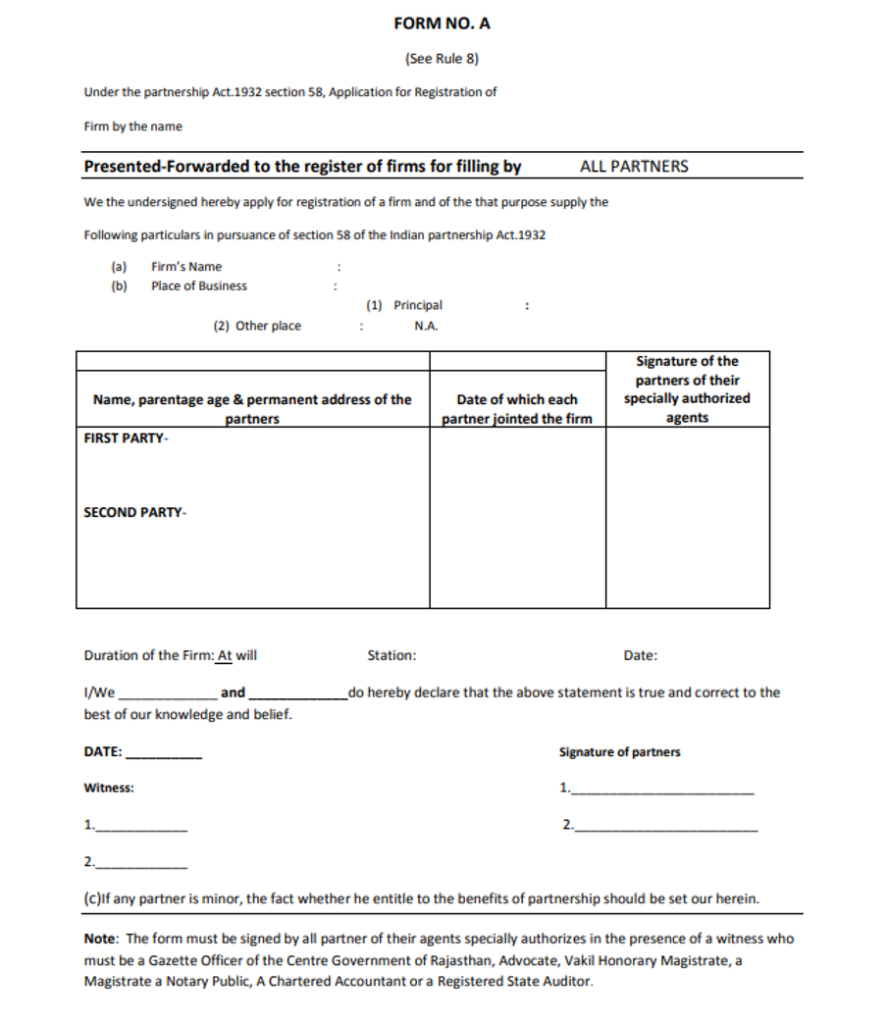
Once you’ve filled out Form A, you’ll need to submit it to the Registrar of Firms along with some supporting documentation. Here’s a list of the documents you’ll typically need:
Make sure to double-check the specific requirements for your state, as some states may ask for additional documents or certifications.
Now that you’ve gathered all the necessary documents, it’s time to submit your application. You can either do this in person at the Registrar of Firms office in your jurisdiction or, in many states, you can also apply online.
If you’re submitting the documents in person, make sure to bring all originals along with photocopies. The originals will be returned to you after verification. Once your application is submitted, the Registrar will review the documents to ensure that everything is in order.
In case you’re applying online, scan all your documents and follow the portal’s instructions for uploading them. Some online systems even allow you to track your application status, so you’ll know exactly when your registration is complete.
You’ll need to pay a registration fee when you submit your partnership deed for registration. The fee varies depending on the state in which you are registering, but it’s usually quite reasonable. For example, in some states, the fee might range from Rs. 200 to Rs. 1,000 depending on the type of partnership and the size of your firm.
The payment can typically be made in cash or through demand draft if you’re applying in person. If you’re going the online route, you’ll likely be able to pay through net banking or a credit/debit card. Once the fee is paid, you’ll receive an acknowledgment slip that confirms your application has been submitted for review.
After reviewing your application and verifying the documents, the Registrar of Firms will officially approve your partnership deed. Once everything is in order, they will issue a Certificate of Registration, which serves as legal proof that your partnership is now registered.
This certificate is incredibly important—it not only gives your business legal recognition but also allows you to open a bank account in the firm’s name and access various government benefits for registered firms. Keep it safe, because you’ll need it for future reference.

Registering a partnership deed in India might seem a little intimidating at first, but once you break it down into these easy steps, it’s actually quite manageable. By drafting a solid partnership deed, submitting the correct documents, and paying the registration fee, you’re well on your way to building a strong and legally sound business foundation.Whether you choose to register your deed online or in person, remember that the time and effort you invest in this process will pay off by giving your business legal backing and avoiding potential conflicts. So, get your documents in order, follow the steps, and you’ll have your Certificate of Registration in hand before you know it!
To read similar articles, click here: https://tmwala.com/blog-partnership-registration/
Link to the Supreme Court’s website: https://www.sci.gov.in
Get started instantly
"*" indicates required fields

TMWala
Your one stop shop for all your business registration and compliance needs.
"*" indicates required fields
Choose your Entity Type
Non-MSME/ Large Entitie
Individual/ MSME/ Sole Proprietorships

₹9,000.00 Original price was: ₹9,000.00.₹3,999.00Current price is: ₹3,999.00.
Trademark Application @ ₹3999* (Premium Discounted Plan for MSME/Individual/Sole Proprietorships) Comprehensive
Government Fees
₹4500/-

₹9,000.00 Original price was: ₹9,000.00.₹3,999.00Current price is: ₹3,999.00.
Trademark Application @ ₹3999* (Premium Discounted Plan for Non-MSMEs/Large Entities) Comprehensive
Government Fees
₹9000/-
Choose your Entity Type
Individual/ MSME/ Sole Proprietorships
Non-MSME/ Large Entities
₹3,500.00 Original price was: ₹3,500.00.₹1,999.00Current price is: ₹1,999.00.
Government Fees
₹4500/-
₹3,500.00 Original price was: ₹3,500.00.₹1,999.00Current price is: ₹1,999.00.
Government Fees
₹9000/-
Choose your Entity Type
Individual/ MSME/ Sole Proprietorships
Non-MSME/ Large Entities

₹1,500.00 Original price was: ₹1,500.00.₹999.00Current price is: ₹999.00.
Trademark Application @ ₹999* (Basic Discounted Plan for MSME/Individual/Sole Proprietorships) Best-Selling, Economical & Easy

₹1,500.00 Original price was: ₹1,500.00.₹999.00Current price is: ₹999.00.
Trademark Application @ ₹999* (Basic Discounted Plan for Non-MSMEs/Large Entities) Best-Selling, Economical, Quick and Easy